近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院博士生周君慧和敖志敏教授在异质结g-CN/MXene光催化降解VOCs的理论研究方面取得了新的研究进展,研究成果以“First-Principles Evaluation of Volatile Organic Compounds D-egradation in Z‑Scheme Photocatalytic Systems: MXene and Graphitic-CN Heterostructures”为题发表于SCI期刊《ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces》。
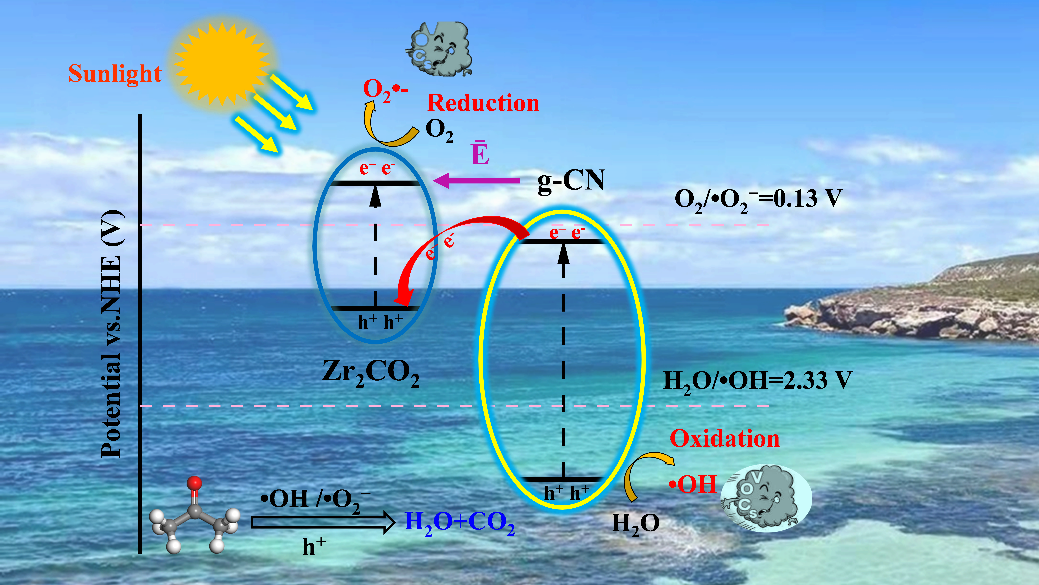
目前,通过实验手段可以有效测试光催化剂的性能并阐述相应的光催化机理,但要在电子或者原子水平上剖析光催反应过程,进而阐明内在的光催化机理是一个巨大的挑战。此外,传统的催化剂开发过程,包括催化剂合成、表征、以及催化剂对污染物处理效果的测试等,需要耗费大量的时间和资源。相对比较而言,现代计算化学工具,密度泛函理论(Density Functional Theory, DFT),为我们提供了更为快捷和经济的研究方式。基于此,本研究以DFT为基础,通过将2D材料g-CN和MXene相结合,构建了新型的Z型异质结g-CN/MXene,并从DFT计算的角度总结提出了评价光催化剂降解VOCs性能的方法。对于评价体系的确定,首先是通过计算本征材料和复合材料的能带结构、氧化还原电位、光吸收谱以及复合催化剂的轨道来判定自由基的产生能力、太阳光的利用率以及催化剂内部的电子转移情况;进而计算H2O、O2以及VOCs在异质结表面的吸附性能;最终在原子水平上探讨催化剂光催化降解VOCs的内在机理。该工作中电子从g-CN的导带转移至Zr2CO2的价带的现象说明该催化剂为典型的Z型异质结,可以有效抑制电子空穴对的分离,并提高光生电子的利用率。此外,相比于本征g-CN和Zr2CO2,异质结g-CN/Zr2CO2可以有效提高可见光利用率并且促进•O2−和•OH自由基的生成,进而攻击VOCs的活性位点,最终将其矿化成CO2和H2O。本研究以g-CN/MXene为例,从DFT计算的角度提出了一种评价光催化剂性能的方法,并探讨了其在光催化降解VOCs方面的研究,该工作不仅可以为VOCs降解催化剂的选择提供理论指导,并有望为MXene材料早日应用于工业领域作出贡献。
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c05617
图表摘要:
论文英文摘要:
It is a formidable challenge to use the traditional trial-and-error method to identify suitable catalysts for the photocatalytic degradation ofvolatile organic compounds(VOCs). In this work, by performingdensity functional theory (DFT)calculations, we designed three Z-schemeg-CN/M2CO2(M = Hf, Zr and Sc) heterostructures, which not only exhibit favorable structure stability, but also show promising ability for photocatalytic degradation of VOCs. The enhancement of photocatalytic activity of these three Z-scheme systemscan be ascribed to the low recombination rate of electron-hole pairs due to photo-electrons migrated from g-CN layer to M2CO2layer and as well as the internal electric fields in the Z-scheme heterojunction. Among the three heterostructures, onlyg-CN/Zr2CO2presents favorable spectra utilization under photo irradiation as well as the direct band gap. As a result, in the Z-schemeg-CN/Zr2CO2heterostructure, the electrons in theconduction band (CB)of g-CN migrate to the holes invalence band (VB)of Zr2CO2layer, which improves extraction and utilization of photo-generated electrons in g-CN sheet. Moreover, theZ-schemeg-CN/Zr2CO2systemshows superior performance for photocatalytic VOCs degradation in comparison with individual g-CN andZr2CO2, which can be attributed to the enhanced VOCs adsorption capacity as well as excellent ability to photo activate O2and H2O into•O2−and •OH radicals. Our findings pave a new promising way to facilitate the application of MXene-based materials for VOCs photocatalytic degradation.
资助项目:
本研究受到国家自然科学基金(21777033和41807191)、广东省自然科学基金(2018A030310524)、广东省科学技术计划项目(2017B020216003)、广东省“珠江人才计划”本土创新科研团队项目(2017BT01Z032)以及广东省教育厅创新团队项目(2017KCXTD012)的资助。