近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队题为《New advance in the application of compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA) in identifying sources, transformation mechanisms and metabolism of brominated organic compounds》的综述性论文在Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology (CREST,http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2021.1993053 )杂志上发表。论文的第一作者为熊举坤博士,第二作者为李桂英教授,通讯作者为安太成教授。该综述全面系统地阐述了单体稳定同位素分析技术示踪溴化有机化合物来源、转化机制以及生物代谢等环境地球化学领域的最新研究进展和挑战,综述内容包括单体C、H、O和Br稳定同位素分析方法和单体稳定同位素分析技术示踪溴化有机化合物来源、转化机制以及生物代谢等方面的应用。同时综述论文还对单体稳定同位素分析技术在环境地球化学领域未来的发展机遇与挑战提出了展望。

溴化有机化合物来源于自然界和人类活动,在环境中广泛并大量存在。大多数溴化有机化合物是危险品,对人类和环境具有极大的风险。而溴化有机化合物的控制需要对他们的环境来源、行为和最终归趋有清晰的认识。近年来,单体稳定同位素分析技术是环境科学、生态学和环境地球化学等诸多研究领域科学突破的一项重要的新工具,可以帮助科学家阐明溴化有机化合物的环境来源、转化机制和归趋等环境地球化学过程。特别是近二三十年来,气相色谱接口燃烧串联同位素比值质谱仪和气相色谱串联多接收感应耦合等离子体质谱仪的出现,极大的发展了单体稳定同位素分析技术在分析溴化有机化合物稳定同位素方面的应用。本综述首先论述了目前单体稳定同位素分析技术分析有机化合物单体碳、氢、氧和溴稳定同位素的分析方法。然后,综述论述了单体稳定同位素分析技术在识别溴化有机化合物来源、示踪溴化有机化合物转化机制和生物代谢等环境地球化学领域的应用。同时,基于化学的反应机理,讨论了其动力学同位素效应(KIEs)。最后,该综述强调了溴稳定同位素效应、多维稳定同位素富集因子和特定位置同位素分析,展望了单体稳定同位素分析技术在环境地球化学领域未来挑战和前景。
论文DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2021.1993053
图文摘要:
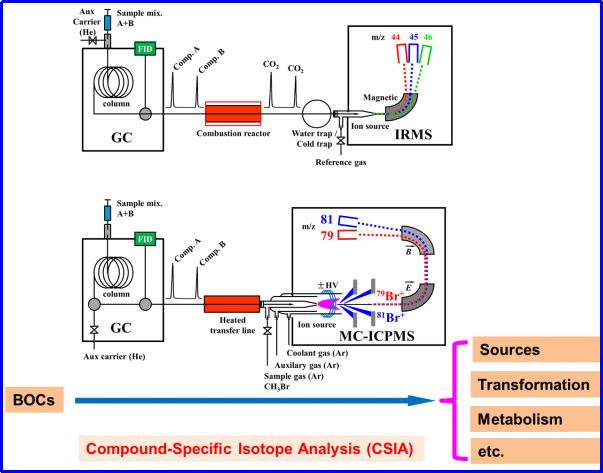
英文摘要:
Brominated organic compounds (BOCs) originate from nature and anthropogenic activities and are plentiful in the environment. Most BOCs are hazardous and pose significant risk to the environment and human health. Controlling these pollutants requires understanding their sources, behaviors, and final environmental fates. Compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA), which has been a new important tool for scientific breakthrough in many research areas, such as environmental, ecological, and geochemical sciences, can help scientists elucidate the sources, transformation pathways and fates of BOCs. The appearance of gas chromatography combustion isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/C/IRMS) andgas chromatographymultiple collectors inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (GC/MC/ICPMS) in the past decades, has greatly developed the application of CSIA for the stable isotope analysis of BOCs. This review first describes the current analytical methods for measuring the carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and bromine stable isotopes of BOCs using mass spectrometry. Then, the review discusses the application for identifying sources, tracing transformation pathways and biological metabolisms. This includes a discussion of the kinetic isotope effects (KIEs), evaluated using (bio)chemical reaction, based on the reaction mechanism. Finally, the review highlights the future challenges and prospects regarding bromine isotope effects, multiple isotope enrichment, and position-specific isotope analysis. This review ends with a perspective on future activities that may benefit the development of the fast-growing field of CSIA.
项目资助:本研究受到国家自然科学基金委项目(41991312,42177192,41731279和41703089)以及国家重点研发项目(2019YFC1804504和2019YFC1804503)的资助。