近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队题为《Adsorption and Desorption Mechanism of Aromatic VOCs onto Porous Carbon Adsorbents for Emission Control and Resource Recovery: Recent Progress and Challenges》的学术论文在Environ. Sci.: Nano (https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00929J)杂志上接受发表。论文的第一作者为张卫平博士,通讯作者为安太成教授。该综述从工业过程苯系物VOCs的排放特征出发,详细阐述了苯系物VOCs在多孔碳材料上的吸附-脱附特征和机理,并系统陈述了吸附-脱附过程中吸附质与吸附剂之间的相互作用机制、吸附剂的失活过程及关键原理等,并仔细总结了基于吸附-脱附原理的集成技术在VOCs排放控制和资源化回收方面的应用。最后,该综述论文还对典型工业VOCs在排放控制和资源化回收实践等方面的发展机遇与挑战提出展望,希望能够为工业废气中VOCs高效的排放控制技术和资源回收技术提供有价值的参考。

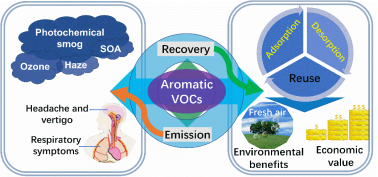
随着工业化和城市化进程的快速发展,往往会导致挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)排放量的急剧增加,特别是苯系物VOCs的排放,不仅会造成环境污染和人类健康危害,同时也是一种严重的资源浪费。在这种背景下,迫切需要采取一些科学的策略来消除或利用这些挥发性有机化合物。其中,实现VOC排放控制的两个重要策略是VOC的吸附和动态脱附行为,这是捕获有价值的VOC或去除无价值的VOC的关键过程。本文系统总结了气态苯系物VOCs在不同多孔碳上的选择性吸附的研究现状,特别是对吸附过程中吸附质与吸附剂之间的相互作用机制及关键影响因素进行了综述。此外,对影响苯系物VOCs脱附的关键影响因素进行了阐述,并基于吸附剂和吸附质相互作用机制,论述了多孔碳在苯系物VOCs吸附-脱附过程中的失活和再生的机制。最后,基于吸附-脱附的相关原理及集成技术,探讨了多孔碳吸附剂在VOCs的排放控制和资源回收过程中的应用。综上所述,本文结合实际工业过程苯系物VOCs排放特征以及环境基础科学中苯系物VOCs在各类多孔碳上的吸附-脱附特征及机制,力争为工业废气中VOCs的高效减排和回收技术提供有价值的技术参考。
论文的网址: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00929J
Graphic Abstract:
论文英文摘要:
As is universally acknowledged, the fast advances in industrialization and urbanization have caused the rapid increase in the emission of aromatic volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which has results in not only much environmental pollution and human health hazard, but also a significant waste of resources. Under such circumstance, it is urgent that some scientific strategies should be adopted to eliminate or reuse those VOCs. Two important strategies of VOC emission control are adsorption and dynamic desorption on porous carbon adsorbents (PCAs), which help to capture valuable VOCs or remove unvalued VOCs. In this review, the research developments of selective adsorption of gaseous aromatic VOCs onto different porous PCAs were systematically reviewed, especially in the interaction mechanism between adsorbates and adsorbents during the adsorption process. Besides, the critical influential factors for the desorption of aromatic VOCs onto PCAs are also discussed, and the mechanisms focused on deactivation and regeneration of PCAs associated with the interaction mechanism of adsorbents and adsorbates are presented. Finally, the integrated process based on adsorption and desorption for emission control and resource recovery is carefully summarized. Overall, this review expounds the characteristics of adsorption and desorption of aromatic VOCs on various PCAs as well as the integrated technologies for emission control and resource recovery of industrial VOC exhaust. We hope this work can lay the base for the efficient abatement and recovery technologies of VOCs from industrial exhaust.
项目资助:该研究工作得到了广东省本土创新团队(2017BT01Z032),国家自然科学基金(42020104001和42007327),广东省基础与应用基础联合基金青年项目(2019A1515110298)和广东省重点研发计划(2019B110206002)等项目支持。