近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队在焦化行业职业暴露相关新型尿液暴露生物标志物的筛查及暴露组学特征研究方面取得最新研究进展,其中2篇研究成果分别以《Nontarget Screening of Novel Urinary Biomarkers for Occupational Exposure to Toxic Chemicals from Coking Industry Using HPLC-QTOF-MS, ES&T, 2023, 57 (35), 13004–13014》和《Coking-Produced Aromatic Compounds in Urine of Exposed and Nonexposed Populations: Exposure Levels, Source Identification, and Model-Based Health Implications, ES&T, 2023, 57 (41), 15379–15391》为题连续发表在Environmental Science & Technology期刊上,而且均被选为内封面文章。论文的第一作者为博士后李海玲,通讯作者为安太成教授。在这项系列研究中,团队人员首先利用液相高分辨质谱技术,基于非靶向分析筛查技术识别出焦化行业职业暴露相关多种新型尿液暴露生物标志物。同时也基于靶向分析技术,系统揭示了焦化职业暴露人群体内芳香族化合物的暴露特征、来源解析及其潜在健康风险。这方面的系列研究为精准评估焦化职业以及其他职业暴露人群体内毒害污染物的健康风险评估和焦化行业污染有效管控提供了重要参考。
期刊内封面图

系列研究成果1:

论文1的网址: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.3c01663.
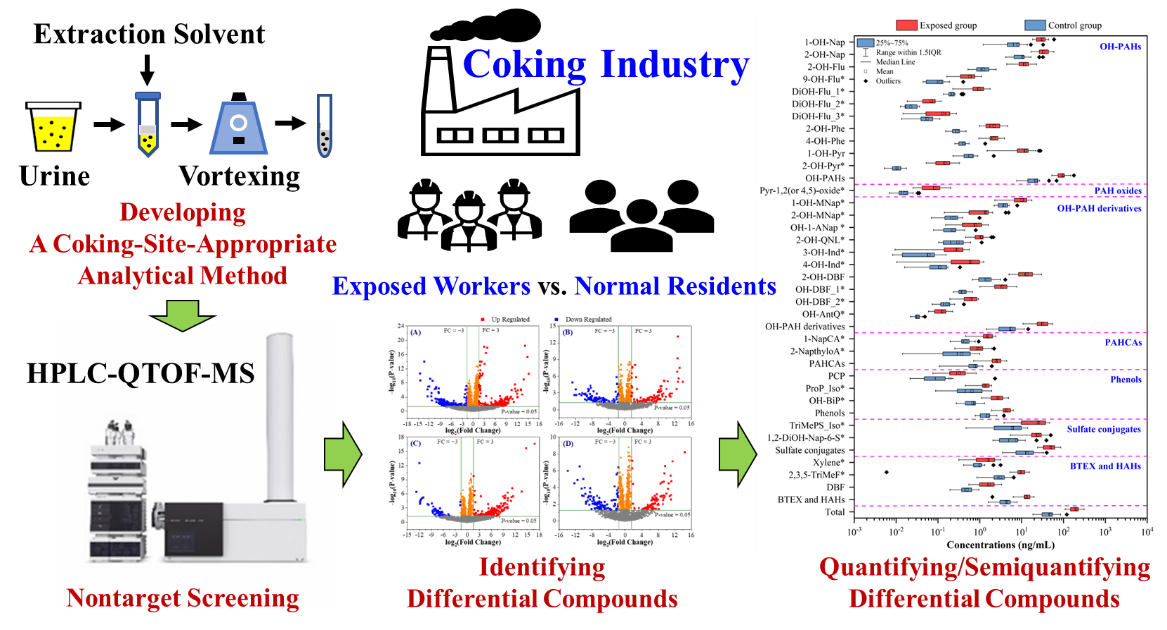
高分辨率质谱是一种用于全面筛查有毒化合物的先进技术。本研究基于采集的焦化场地职业暴露人群和普通居民的尿液样本,旨在鉴定出焦化职业暴露的新型尿液生物标志物。本研究开发了适用于焦化场地的化合物非靶标筛查新方法。通过非靶向筛查,共鉴定出了515个差异特征离子,并最终确认了32个差异化合物作为本研究的候选化合物,其中包括13个多环芳烃(PAH)代谢产物。除了单羟基PAHs(例如1-和2-萘酚,2-和9-羟基芴,2-和4-菲醇,以及1-和2-羟基芘),还检测到了许多其他PAH的代谢产物,包括二羟基代谢产物和PAH氧化物等,这表明仅基于单羟基PAHs的早期定量方法严重低估了PAHs的人体暴露程度。此外,本研究还发现了几种潜在新型焦化场地的生物标志物,包括喹啉-2-醇(1.10 ± 0.44 ng/mL)、萘甲醇(11.4 ± 5.47 ng/mL)、N-羟基-1-氨基萘(0.78 ± 0.43 ng/mL)、羟基二苯并呋喃(17.4 ± 7.85 ng/mL)、羟基蒽醌(0.13 ± 0.053 ng/mL)和羟基联苯(2.70 ± 1.03 ng/mL)等。尽管它们的水平远低于羟基PAHs(95.1 ± 30.8 ng/mL),但其高毒性不容忽视。总体而言,本研究提供了一种场地污染物复合暴露的非靶向筛查方法,用于识别人体尿液中的毒害化合物及其代谢产物,这对于精准评估焦化工业中有毒化合物质的暴露风险和健康防护至关重要。
图文摘要
英文摘要
High-resolution mass spectrometry is an advanced technique for comprehensive screening of toxic chemicals. In this study, urine samples were collected from both an occupationally exposed population at a coking site and normal inhabitants to identify novel urinary biomarkers for occupational exposure to coking contaminants. A coking-site-appropriate analytical method was developed for unknown chemical screening. Through non-target screening, 515 differential features were identified, and finally, 32 differential compounds were confirmed as candidates for the current study, including 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) metabolites. Beside monohydroxy-PAHs (such as 1-&2-naphthol, 2-&9-hydroxyfluorene, 2-&4-phenanthrol, and 1-&2-hydroxypyrene), many other PAH metabolites including dihydroxy metabolites, PAH oxide, and sulfate conjugate were detected, suggesting that the quantification based solely on monohydroxy-PAHs significantly underestimated the human exposure to PAHs. Furthermore, several novel compounds were recognized that could be considered as biomarkers for the exposure to coking contaminants, including quinolin-2-ol (1.10±0.44 ng/mL), naphthylmethanols (11.4±5.47 ng/mL), N-hydroxy-1-aminonaphthalene (0.78±0.43 ng/mL), hydroxydibenzofurans (17.4±7.85 ng/mL), hydroxyanthraquinone (0.13±0.053 ng/mL), and hydroxybiphenyl (2.70±1.03 ng/mL). Despite their lower levels than hydroxy-PAHs (95.1±30.8 ng/mL), their severe toxicities should not be overlooked. The study provides a non-target screening approach to identify chemicals in human urine, which is crucial for accurately assessing the health risks of toxic chemicals in the coking industry.
项目资助:本研究得到国家重点研发重点专项项目(2019YFC1804503)、国家自然科学基金(42207485、41991312、42122057和41907363)、广东省本土创新科研团队(2017BT01Z032)和广东省基础与应用基础研究基金(2021A1515110935)的大力支持。
系列研究成果2:

论文2的网址: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.3c04906.
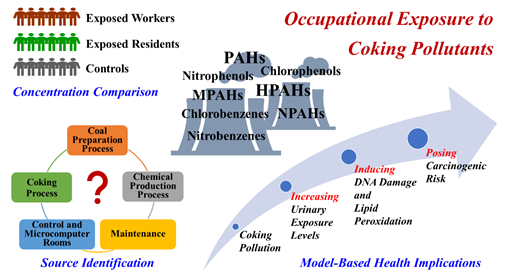
焦化污染问题是我国面临的一个复杂环境问题,给从业人群和周边居民暴露带来了潜在的健康风险。本研究主要通过采集了焦化厂工人、工厂附近居民和远离工厂污染源的对照人群的尿液样本,分别开展了包括多环芳烃(PAHs)及其衍生物的代谢产物、氯酚(CPs)和硝基酚(NPs)在内的25种焦化污染产生的芳香族化合物(ACs)的内暴露特征。发现焦化工人尿液中总ACs的中值浓度为102 ± 0.87 μg·g−1 肌酐,显著高于其他周边居民和对照组人群。羟基PAHs(OH-PAHs)和羟基杂环PAHs(OH-HPAHs)是最主要的ACs。直接暴露于焦化生产工艺的工人,如炼焦、备煤及化工生产工艺工人,尿液中具有更高的OH-PAHs和OH-HPAHs(除5-羟基异喹啉)的浓度,然而间接暴露工人尿液中其他ACs的浓度也较高,表明了这些目标化合物在焦化厂内的不同生产加工工艺过程中的污染来源不同。作者也基于quantile g-computation模型研究发现AC的混合暴露对焦化工人体内DNA损伤及脂质过氧化产生了显著正向效应,其中5-羟基异喹啉和3-羟基咔唑的影响最大。蒙特卡洛模拟结果也表明焦化行业污染导致工人的致癌风险比对照人群增加了~5倍,其中芘、五氯酚及咔唑的贡献最大,炼焦工人的致癌风险也是整个工艺中最高的。因此,本研究可以为未来焦化行业的污染减排和风险管控提供重要参考依据。
图文摘要
英文摘要
Coking contamination in China is complex and poses potential health risks to humans. In this study, we collected urine samples from coking plant workers, nearby residents, and control individuals to analyze twenty-five coking-produced aromatic compounds (ACs), including metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their derivatives, chlorophenols, and nitrophenols. The median concentration of total ACs in urine of workers was 102 μg·g−1 Creatinine, significantly higher than in the other two groups. Hydroxy-PAHs and hydroxy hetero-PAHs were the dominant ACs. Workers directly exposed from coking industrial processes, i.e., coking, coal preparation, and chemical production processes, showed higher concentrations of hydroxy-PAHs and hydroxy hetero-PAHs (excluding 5-hydroxyisoquinoline), while those from indirect exposure workshops had higher levels of other ACs, indicating different sources in the coking plant. The AC mixture in workers demonstrated positive effects on DNA damage and lipid peroxidation with 5-hydroxyisoquinoline and 3-hydroxycarbazole playing a significant role using quantile g-computation model. Monte Carlo simulation revealed that coking contamination elevated the carcinogenic risk for exposed workers by 5-fold compared to controls with pyrene, pentachlorophenol, and carbazole contributing the most, and workers from coking process are at the highest risk. This study enhances understanding of coking-produced AC levels and provides valuable insights into coking contamination control.
项目资助:本研究得到国家重点研发重点专项项目(2019YFC1804503)、国家自然科学基金(42207485)、广东省本土创新科研团队(2017BT01Z032)和广东省基础与应用基础研究基金(2021A1515110935)的大力支持。