近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队在电子垃圾拆解行业中人群吸入典型挥发性和半挥发性有机化合物与肝功能损伤的关联研究中取得最新研究进展,研究成果以《Associations between inhalation of typical volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in e-waste dismantling workers with liver function damage》为题发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials (2024, 464:133004)期刊上。在这项横断面研究中,对电子垃圾拆解工人和居住在拆解现场附近的居民受试者进行了暴露和流行病调查。根据特定污染物浓度和个人暴露水平的评估,计算了他们对挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)和半挥发性有机化合物(SVOCs)的个人吸入暴露。同时,通过分析了他们的血清样本肝功能水平,通过分位g-computation分析吸入暴露对肝功能的影响并使用BKMR模型探讨了其暴露-响应关系,确认VOCs与SVOCs的复合暴露对肝功能损伤存在一定的关联关系。这一研究填补了实际场景下复合暴露的人类群体对于这些化合物影响带来的健康影响方面的认知空白。

论文网址:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133004
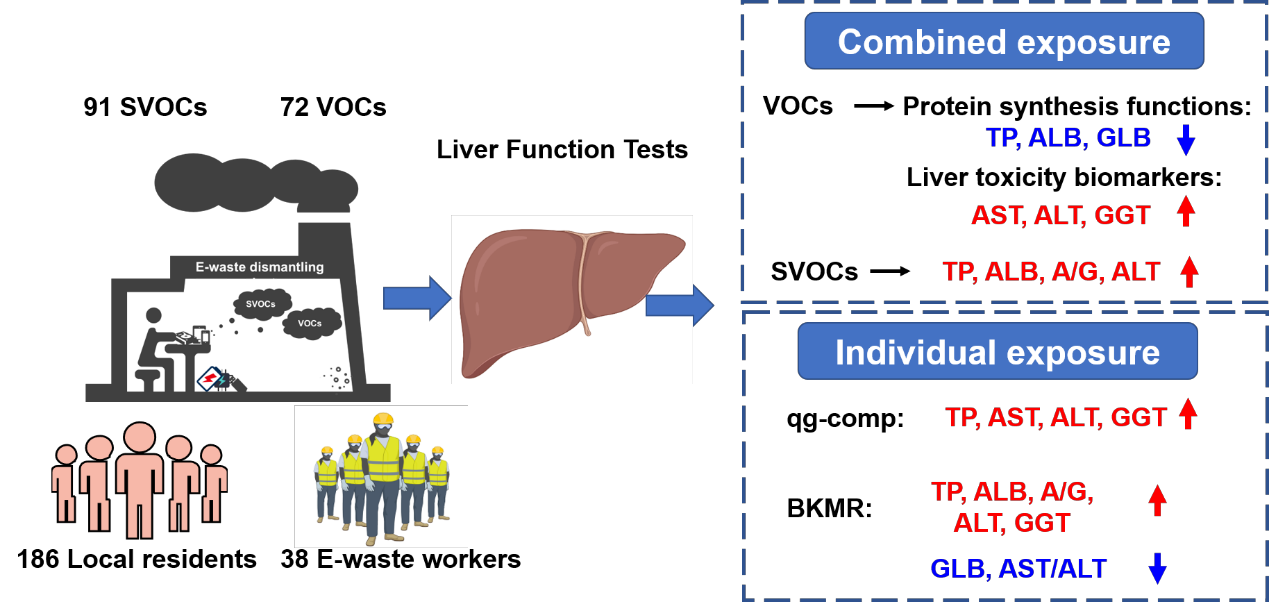
早期的细胞培养和动物模型的研究表明,一些挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)和半挥发性有机化合物(SVOCs)可能对肝脏产生一定的毒性作用,然而在真实实际环境的暴露它们对人群的影响尚未明确。在我们取得的这项横断面研究中,对中国南部一个典型的38名电子垃圾拆解工人和居住在拆解点附近的186名居民,总共224名参与者进行了环境暴露与健康效应评估,探讨了在72种VOCs和91种SVOCs的复合暴露吸入情况的个人暴露水平评估。此外还利用他们的血清样本测定了肝功能测试(LFTs)等参数,包括总蛋白(TP)、白蛋白(ALB)、球蛋白(GLB)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、γ-谷氨酰转肽酶(GGT)和胆红素等指标。通过VOCs/SVOCs的暴露水平与不同LFTs结果的线性回归分析表明:VOC暴露与TP、ALB、GLB水平呈负相关(表明肝脏特定蛋白质合成功能受损),而与AST、ALT、GGT活性呈正相关(标志着存在一定的肝脏损伤)。SVOC暴露不仅与AST和ALT呈正相关,还与TP和ALB呈正相关。所有这些发现得到了g-computation分析的支持,并在贝叶斯核机器回归模型中得到了进一步确认。这项研究表明,VOCs和SVOCs的复合暴露吸入可能在一定程度上损害人体的肝功能。这一研究填补了实际场景下复合暴露的人类群体对于这些化合物影响带来的健康影响方面的认知空白。
图文摘要
英文摘要
Studies in cell culture and animal models suggest hepatotoxicity of some volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs), however, their effects in human populations under real exposure conditions have never been clarified. In this cross-sectional study, 224 participants, 38 e-waste dismantling workers and 186 subjects residing near to the dismantling sites in southern China, were evaluated for personal inhalational exposure to 72 VOCs and 91 SVOCs according to site-specific atmospheric chemical concentrations and personal exposure time. Additionally, their serum samples were subjected to liver function tests (LFTs), including total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), globulin (GLB), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and bilirubin. Linear regression analysis of the VOC/SVOC levels against the LFTs results indicated that VOC exposure was negatively associated with the TP, ALB, GLB levels (indicating liver-specific protein synthesis functions), while positively associated with AST, ALT, GGT activities (marking liver damage). Somehow, SVOC exposure appeared to be positively associated with not only AST and ALT but also TP and ALB. These findings were supported by the quantile g-computation analysis and confirmed in the Bayesian kernel machine regression model. This study indicates that simultaneous inhalation of VOCs and SVOCs may impair human liver functions.